|
|
|
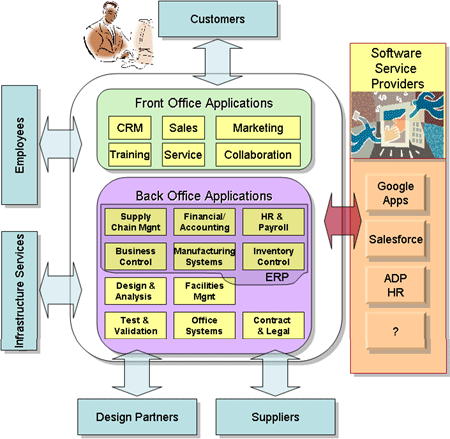
The high level diagram above depicts the conceptual view of SolMed systems/ applications and their relationship to the key actors in the internal and external environment. The “Software Service Providers” represents vendors providing direct services to the enterprise. Typically these services will be re-branded and delivered to users independent of the source. “Design Partners” represents the close interaction with the parent companies, DMC and Welch Allyn. The application architecture must support both onsite and remote collaborative product design with DMC and Welch Allyn.
As a start-up company, SolMed places high demands on IT to deploy a full suite of Business systems over a relatively short period of time. At the same time the company capitalization and business plan constrain the IT resources available to accomplish this task. To be successful the SolMed IT staff must focus on providing lean and efficient solutions. These solutions must be flexible enough to accommodate both changes to the business plan as well as support rapid organizational growth. IT systems can not be allowed to constrain business growth even as business strategies change in response to market forces.
Business systems can be split into two categories: Front Office systems and Back Office systems. Front Office systems support business processes that directly provide a product or service to our customers. Back Office systems support business processes that do not directly interface with our customers.
Software as a service (SaaS) “is a software application delivery model where a software vendor develops a web-native software application and hosts and operates (either independently or through a third-party) the application for use by its customers over the Internet.” Customers pay for using the software NOT for owning the software.
Service oriented architecture describes an architectural approach that uses loosely coupled services to support business needs. Business and application functionality are abstracted into services to promote reuse, autonomy, and ability to build composite functionality.
Four IT principles have been documented to guide the IT system/application architecture effort:
|
|
| Infrastructure services include Voice/phone (VoIP), Network, and Desktop Computing as well as business services develop as part of the SOA approach. |
© 2007 CMU/Boeing Class - all rights reserved