|
Knowledge Management Plan - AS-IS (Current) Situation
The following knowledge management plan attempts to provide an overview of the current state for knowledge management within Kitty Hawk Aeronautics.
A. The approach to managing data, information, and knowledge across the enterprise The current approach within Kitty Hawk Aeronautics for knowledge management is that each LOB unit is responsible for managing their own individual operational data. This includes financial, payroll, and sales data.
B. How data and information sharing support the Business Plan No understanding of how data and information sharing support the Kitty Hawk Aeronautics Business Plan exists at this time.
C. Data and information-sharing strategies and diagrams for each Line of Business Currently, each Line of Business unit is responsible for managing their own operational data.
D. What types of data in the enterprise require extra protection? There is no current data sensitivity guideline or policy defining what types of data require extra protection and what security mechanisms need to be in place at each sensitivity level.
E. The lifecycle for data and information that is key to the success of the enterprise There is no current lifecycle for data and information for Kitty Hawk Aeronautics.
Overall Conclusion Not much is known from an enterprise perspective by Kitty Hawk Aeronautics about the current state of their data. They have no linkage to their Business Plan, no data or information sharing strategies in place beyond each LOB, and no defined policies for how to manage sensitive data or how to address data lifecycle management.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Knowledge Management Plan - TO-BE (FUTURE) Situation
The following knowledge management plan attempts to provide an overview of the desired state for knowledge management within Kitty Hawk Aeronautics. Specifically, it will outline a vision statement, detail how information sharing is linked to its Business Plan, and provide guidelines on data sensitivity and data lifecycle mgmt.
A. The desired approach to managing data, information, and knowledge across the enterprise. The future vision is to establish the following:
From a planning perspective the achievement of the above objectives will require that the following tasks be completed:
Please refer to the Strategic Initiative Medium Level View for goals and initiatives that have been identified within the Kitty Hawk Strategic Plan.
B. How data and information sharing will support the Business Plan? We will accomplish support of the Kitty Hawk Aeronautics Business Plan by making all enterprise information available within the Kitty Hawk Data Warehouse necessary to meet the following data/information categories:
Please refer to the Strategic Initiative Detailed View for specific outcomes that have been identified within the Kitty Hawk Business Plan.
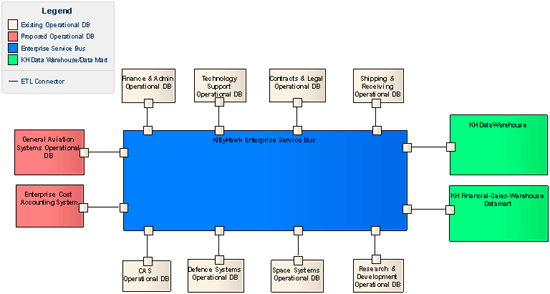
C. What Data and information-sharing strategies and diagrams for each Line of Business will be used? The following data context diagram (below) showing how current and future operational databases, knowledge warehouse, and an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) can be used for sharing, publishing data, information between operational databases and knowledge warehouse.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Overall Description All operational databases displayed above are used to support the day to day operations for each LOB. On a predetermined schedule (daily, weekly, monthly), relevant data from each operational LOB DB shall be extracted, transformed and loaded within the KH Data Warehouse using the Enterprise Service Bus to drive automation of this ETL process. Access to the KH Data Warehouse and KH Financial-Sales-Warehouse Datamart will be through the EA repository using a standard web browser. Daily reports from the KH Financial-Sales-Warehouse Datamart will be delivered to senior mgmt.
Link to the high-level entity-relationship graphical view of the Kitty Hawk Data Warehouse Link to the data dictionary view of the Kitty Hawk Data Warehouse
Other Considerations
D. What types of data in the enterprise require extra protection? Data shall be evaluated to determine its sensitivity level based upon the following attributes:
Once the sensitivity level for the data has been determined the following table of recommended safeguards shall be used to select and determine the appropriate level of security that will need to be applied to safeguard the data.
Table 1 - Data Sensitivity Table |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
These guidelines must be reviewed every three years and, if necessary, updated to provide an acceptable level of data sensitivity for the enterprise.
For a more detailed understanding of the Kitty Hawk information security policies please follow the provided link here to the Security Solutions, Detailed View.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
E. The lifecycle for data and information that is key to the success of the enterprise Data shall have its lifecycle classification determined using the following table below. The classification assigned to the data shall be used to determine the lifecycle policy assigned to the data (e.g. how long it needs to be maintained). Table 2 Data Lifecycle Table |
|||||||||||||||
|
© 2008 CMU/Boeing Class - all rights reserved